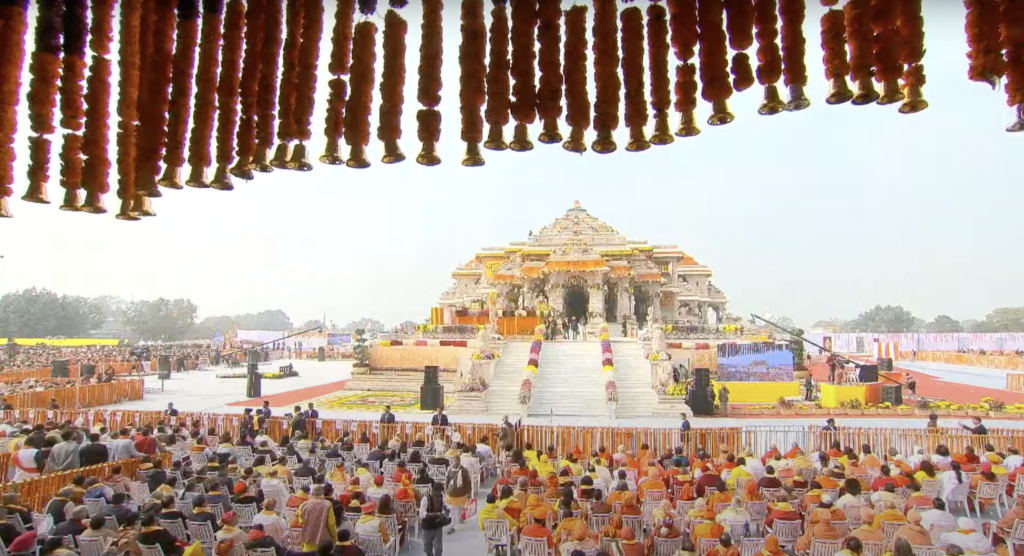
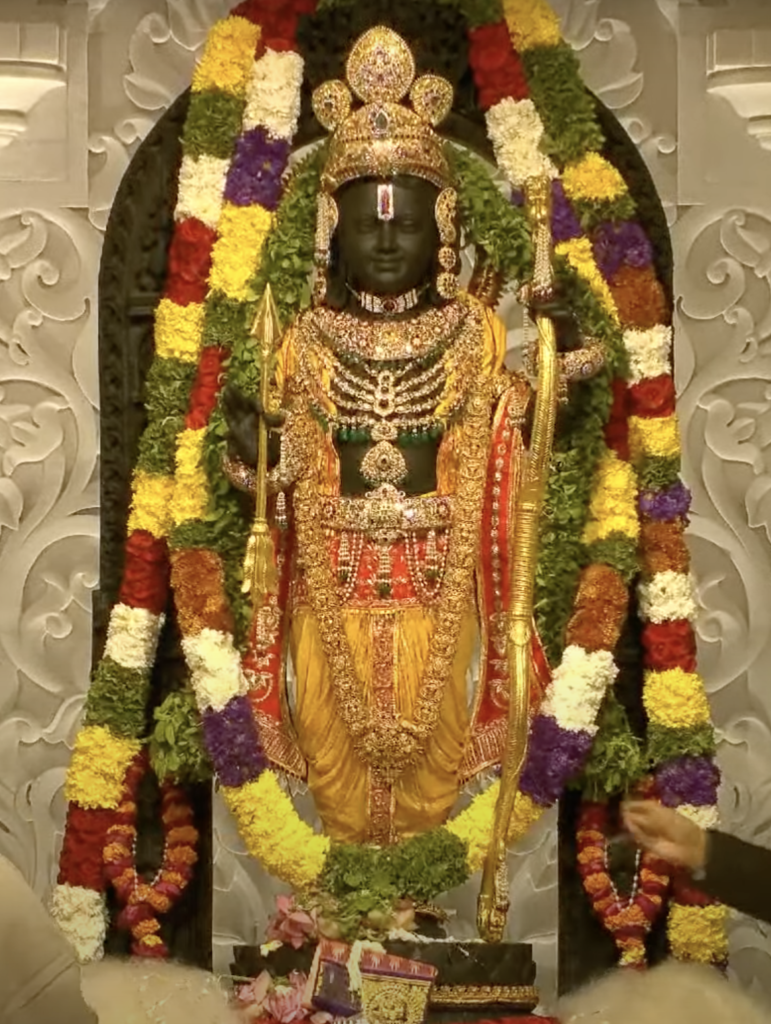
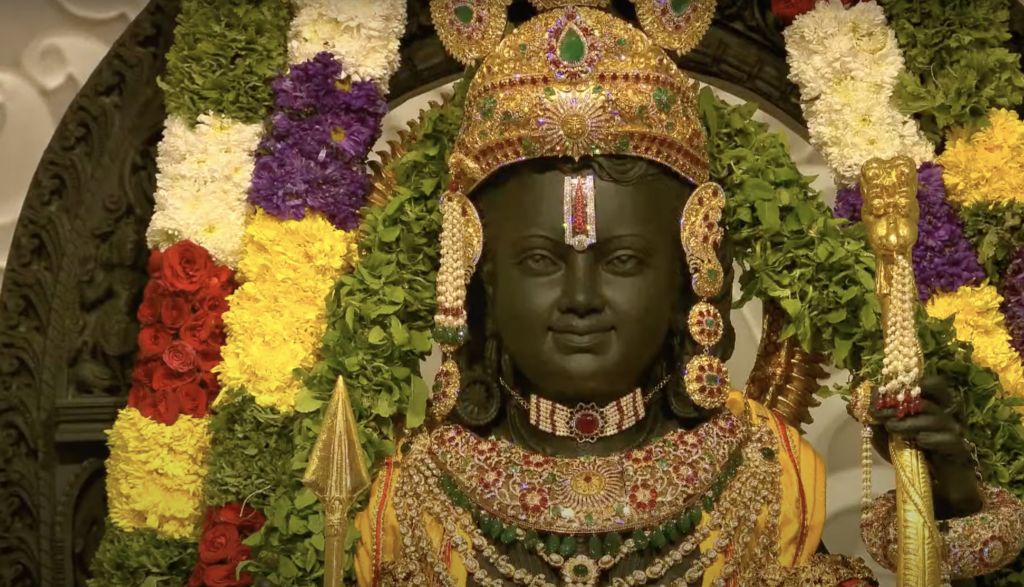
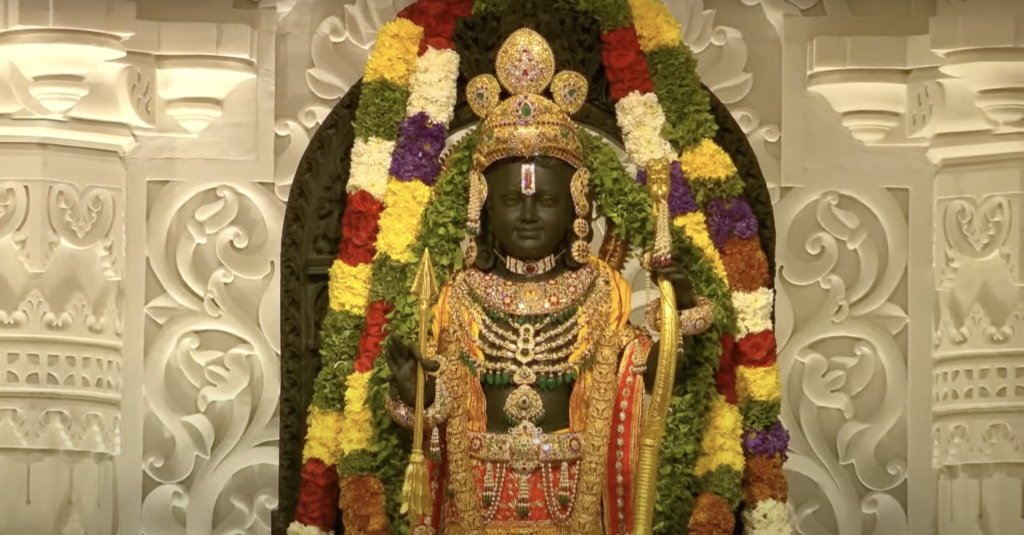
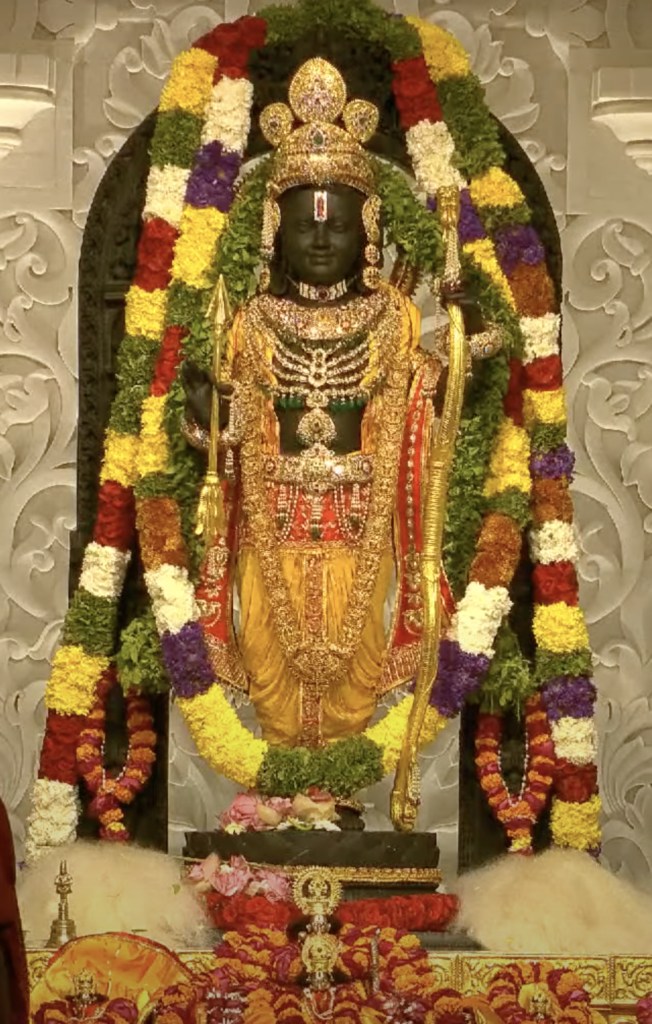
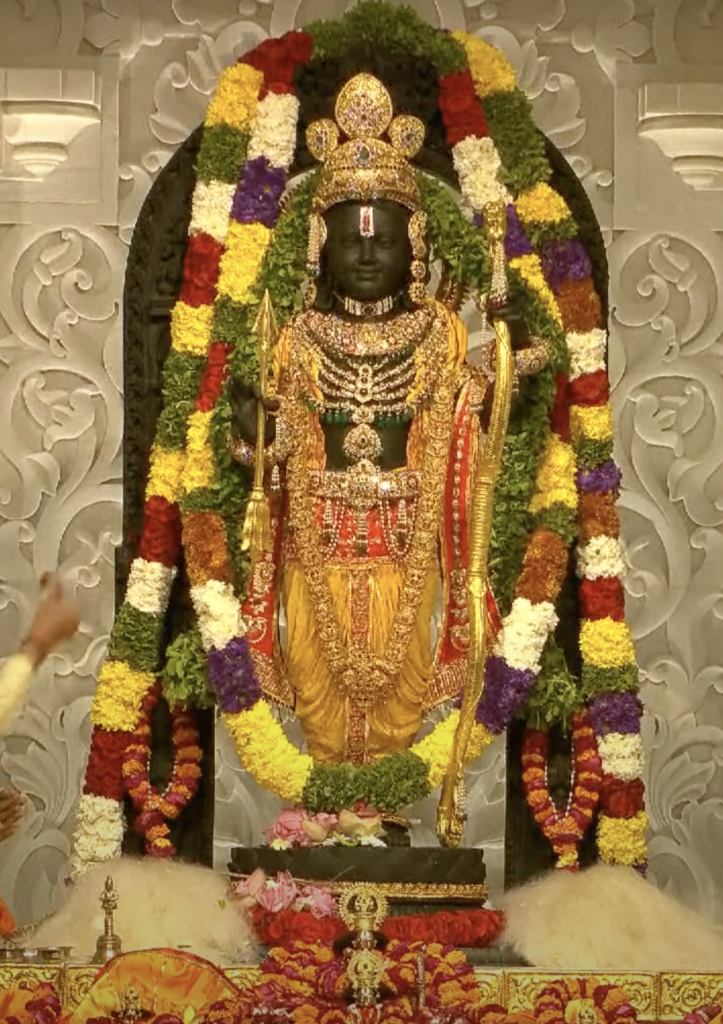
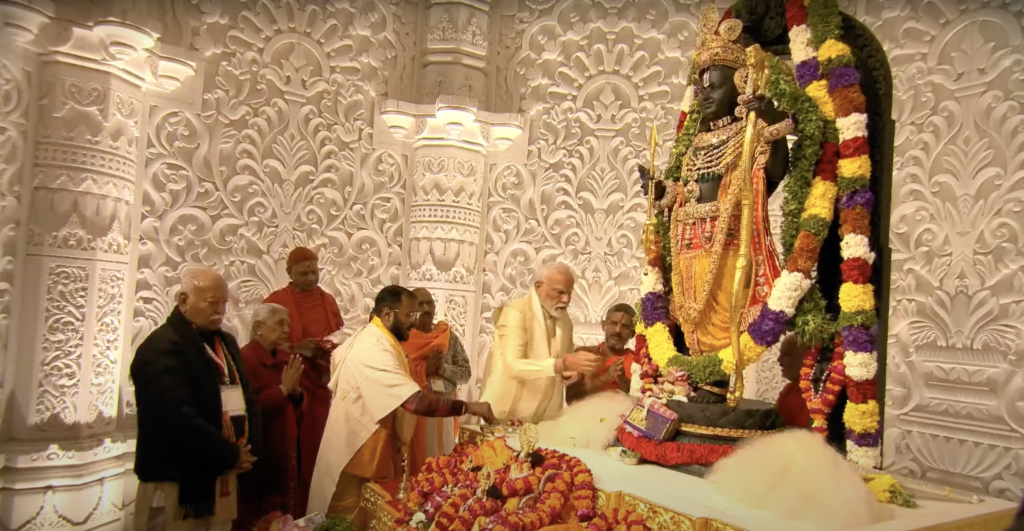
Ram Mandir: A Symbol of Faith
The Ram Mandir, or Ram Temple, is a Hindu temple in Ayodhya, Uttar Pradesh, India. It is dedicated to Lord Ram, one of the most revered deities in Hinduism and the hero of the epic Ramayana. The temple was inaugurated by Prime Minister Narendra Modi on January 22, 2024, after a long and bitter legal dispute over the ownership of the land where it stands.
The ancient city of Ayodhya stands as a testament to India’s rich cultural and religious heritage, with its roots deeply embedded in the epic Ramayana. At the heart of Ayodhya’s significance lies the revered figure of Lord Rama, whose life and teachings continue to shape the spiritual and moral fabric of millions. In this article, we delve into the timeless connection between Ram and Ayodhya, exploring the historical and cultural dimensions that make this relationship so profound.
Historical Perspective:
Ayodhya, one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world, is situated on the banks of the sacred Sarayu River in the northern Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is believed to be the birthplace of Lord Rama, the seventh avatar of Lord Vishnu, according to Hindu mythology. The Ramayana, an ancient Indian epic, narrates the life of Rama, his exile, the abduction of his wife Sita by the demon king Ravana, and the eventual triumph of good over evil.
The Ramayana, composed by the sage Valmiki, has been a source of inspiration and guidance for millions of people over the centuries. It transcends religious boundaries and has become an integral part of India’s cultural identity. The story of Lord Rama’s life is not just a religious narrative but a moral compass that has guided individuals in their personal and social lives for generations.
Ayodhya as a Pilgrimage Site:
For devout Hindus, Ayodhya is not just a historical city but a sacred pilgrimage site. The city is dotted with temples and shrines dedicated to Lord Rama, where pilgrims from across the country come to seek blessings and immerse themselves in the divine atmosphere. The Ram Janmabhoomi, believed to be the birthplace of Rama, holds particular significance. The Babri Masjid, built in the 16th century, stood at this site until its demolition in 1992, sparking a prolonged and contentious legal battle over the land.
Legal Disputes and the Ayodhya Verdict:
The Ayodhya dispute, involving competing claims by Hindus and Muslims over the Babri Masjid-Ram Janmabhoomi site, spanned several decades and was a source of social and political tension in India. In 2019, the Supreme Court of India delivered a landmark verdict, allocating the disputed land for the construction of a Hindu temple dedicated to Lord Rama and providing an alternate site for the construction of a mosque.
The verdict was hailed as a step towards resolving a longstanding issue that had fueled communal tensions. It emphasized the need for communal harmony and respect for the diverse religious beliefs of India’s citizens. The construction of the Ram Temple at the Ayodhya site is seen as a significant moment in the history of India, symbolizing religious coexistence and the triumph of dialogue over discord.
Cultural Impact:
The story of Ram and Ayodhya has transcended religious and cultural boundaries, leaving an indelible mark on literature, art, music, and dance. The Ram Leela, a dramatic retelling of the Ramayana, is performed across the country during the festival of Navaratri. The teachings of Rama, encapsulated in the Ramayana, continue to inspire philosophical thought and moral values.
Ayodhya serves as a cultural hub, hosting various events and festivals that celebrate the spirit of Lord Rama. The city’s rich history and association with the epic have made it a focal point for cultural exploration, drawing scholars, artists, and tourists alike.
The timeless connection between Ram and Ayodhya stands as a testament to the enduring power of faith, culture, and heritage. The epic tale of the Ramayana, with Ayodhya at its core, has shaped the spiritual and moral ethos of millions, providing a guiding light for generations. The resolution of the Ayodhya dispute and the construction of the Ram Temple marks a significant chapter in India’s history, emphasizing the importance of dialogue, coexistence, and the preservation of cultural heritage. As Ayodhya continues to evolve, it remains a symbol of unity in diversity, a place where the divine and the earthly converge to create a tapestry of faith and tradition.